What Is An HRC Fuse
Definition: The HRC fuse whose full name is the High Rupturing Capacity fuse is similar to a normal fuse in which the fuse wire carries a short circuit current up to a certain limit. If the flow exceeds this, it burns. HRC fuses are made from glass or some other type of chemical compound.
The fuse is tightly closed to prevent atmospheric air from entering it. The ends of the fuse are made of ceramic metal caps which are attached with flexible silver wire. There is a large amount of space on the inside of this which is around the wire otherwise the element of the fuse.
The HRC fuse is uniform, has the feature that it has a very low tripping time if it has a high-pressure current. Similarly, if the fault current is not high, the break time is long.
Construction of HRC Fuse:
The HRC fuse is made of a material that has a high heat-resistant body like a ceramic. Metal-end caps are added to this ceramic body. Which is connected by an element carrying a silver currently.
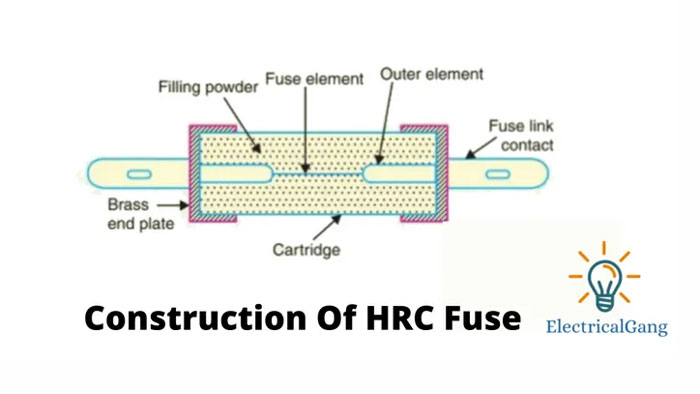
The inside of the fuse body is filled with powder which contains the materials used such as quartz, plaster Paris f Paris, dust, marble, chalk, etc. Noise Causes The essence cannot overheat within the current. The heat generated evaporates the dissolved element.
The chemical reaction will take place between the filling power and the silver vapor, resulting in a high resistance material to help reduce the arc inside the fuse. Copper or silver is usually used in fuse due to their low resistance. A fuse element usually has two or more sections that are connected with the help of a tin.
The melting point of tin is 2400° C which is less than the melting point of silver like 980° C thus melting point of tin joints prevents fuse from getting high temperatures in case of short circuit and overload.
Working Principle of HRC Fuse:
Under normal conditions, the current does not generate enough heat to dissolve it. If more current passes than its limit the fault current melts the element of the fuse before it reaches its climax. When the fuse is in an overload condition the fuse ingredient does not melt but if such a condition lasts for a long time then a material like eutectic will melt and break the fuse element.
The thinner parts of the fuse element melt faster in a smaller area when the fuse is in a short circuit condition. And it will break before the eutectic material. HRC, therefore, has reason to provide limitations within the element of the fuse.
Type of HRC fuse:
There are usually 3 types of fuses that are listed below:
|
Sr.No. |
Type of HRC fuse |
|
#1 |
NH Type Fuse |
|
#2 |
DIN Type Fuse |
|
#3 |
Blade Type Fuse |
#1. NH Type Fuse:
NH type fuse is used for low and medium voltage. This provides protection in situations like overload and short circuits. This fuse protects the motor’s starting as well as other devices against overload and short circuits. These fuses are available in lightweight with specific parameters.
#2. DIN Type Fuse:
These are available in a wide range of electric currents. It is used in different temperatures with different properties. These are available in a variety of voltages and are used to protect the transformer.
Its cleaning capacity is best for perfect with short-circuit act. Used in air and mining, feeder partitioning, gas-insulated switchgear, and transformers.
#3. Blade Type Fuse:
This type of fuse is also known as plug I. The fuse is available with a plastic body and two metal caps to set in the socket. It is used in cars to protect against short circuits, wiring, and motors for backup protection.
These are available in low weights and currently include low cutoffs. Blade-type fuses are available in different sizes and shapes with the capacity of different current ratings.
Characteristics of HRC Fuse:
A fuse works after the element dissolves due to the heat generated by the I2RF in which the RF blocks the fuse. If the current exceeds the capacity of the fuse, its heat also increases.
Therefore, in a state of more current, the fuse melts faster. Thus, the relationship between the time-current of the fuse is named as the fuse characteristics. For proper selection of fuse, it is very useful for a particular circuit.
Advantage of HRC Fuse:
The Advantages of the HRC fuse are as follows:
• Cheaper compared to other fuses.
• The design is straightforward and simple.
• Maintenance of any kind is not required.
• Easy working.
• This program is ongoing.
• High breaking capacity.
• The in-time characteristic is perfect for overload protection.
Disadvantages of HRC Fuse:
The disadvantages of the HRC fuse are as follows:
• This cannot be reused once exited.
• It causes overheating for close contacts.
• After each action, they will change.
• The probability of interlocking is high.
• The heat generated by the arc can affect the connected switches.
Disadvantages of HRC Fuse:
The disadvantages of the HRC fuse are as follows:
• This cannot be reused once exited.
• It causes overheating for close contacts.
• After each action, they will change.
• The probability of interlocking is high.
• The heat generated by the arc can affect the connected switches.
1. What are the types of HRC fuses?
There are usually 3 types of fuses that are listed below:
|
Sr.No. |
Type of HRC fuse |
|
#1 |
NH Type Fuse |
|
#2 |
DIN Type Fuse |
|
#3 |
Blade Type Fuse |
2. What is the advantage of HRC Fuse?
The Advantages of the HRC fuse are as follows:
• Cheaper compared to other fuses.
• The design is straightforward and simple.
• Maintenance of any kind is not required.
• Easy working.
• This program is ongoing.
• High breaking capacity.
• The in-time characteristic is perfect for overload protection.
3. What does HRC fuse mean?
Definition: The HRC fuse whose full name is the High Rupturing Capacity fuse is similar to a normal fuse in which the fuse wire carries a short circuit current up to a certain limit. If the flow exceeds this, it burns. HRC fuses are made from glass or some other type of chemical compound.
4. What are the disadvantages of the HRC fuse?
The disadvantages of the HRC fuse are as follows:
• This cannot be reused once exited.
• It causes overheating for close contacts.
• After each action, they will change.
• The probability of interlocking is high.
• The heat generated by the arc can affect the connected switches.





