What Sizes Of Fuses You Need In Your Solar Array
This blog post is going to teach you how to determine when and if you need to add in-line fuses when designing a camper solar array. Sometimes you need to fuse your solar array, and sometimes you don’t. There’s quite a bit of reasoning behind the decision, but ultimately… the NEC (National Electric Code) makes the decision for us. By the end of this blog post you will know when, where, and what sizes of fuses you need in your solar array.
Fusing a Solar Array
The National Electric Code is pretty straightforward on this issue in NEC 690.9 (A) (2020 Edition) and says (Paraphrased for clarity):
Solar arrays having higher current availability (parallel strings of solar panels) than the maximum overcurrent protective device rating specified for the panel shall be protected from overcurrent. EXCEPT when the short circuit currents from all sources do not exceed the ampacity of the wires and maximum overcurrent protective device size rating specified on the PV module nameplate.
690.9 Overcurrent Protection.
(A) Circuits and Equipment. PV systcm dc circuit and imverter output conductors and equipment shall be protecied against overcurrent. Circuits sized in accordance with 690.8(A)(2) are required to be protected against overcurrent with overcurrent protective devices. Fach circuit shall be protected from overcurrent in accordance with 690.9(A)(1), (A)(2), or (A)(3).
(1) Circuits Where Overcurrent Protection Not Required.
Owercurrent protective devices shall not be required where both of the following conditions are met:
(1) The conductors have sufficient ampacity for the maximum circuit current.
(2) The currents from all sources do not exceed the maximum overcurrent protective device rating specifed for the PV module or clectronic power converter.
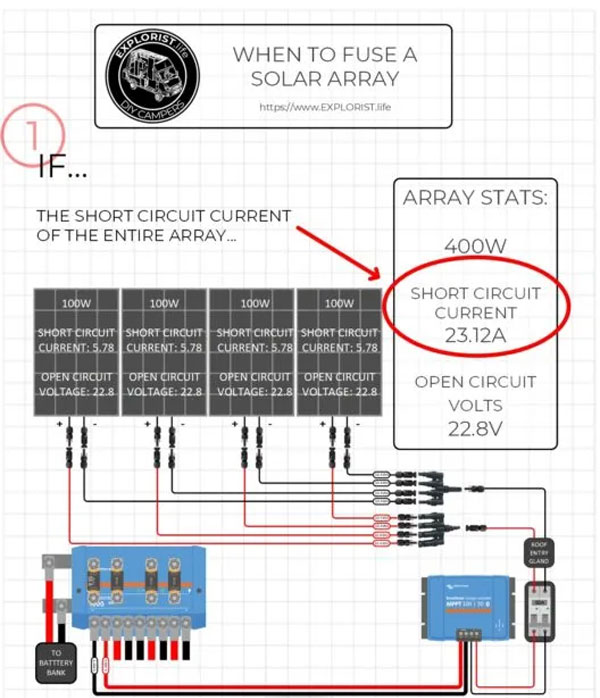
KEY TAKEAWAY: This means that if the Short Circuit Current of the entire solar array is GREATER than the Maximum Series Fuse Rating on the solar panel label, each parallel connected panel (or series string) must be fused.
This means you need two things to determine if your solar array needs to be fused:
•The Short Circuit Current of your Solar array.
•The Maximum Series Fuse Rating of your Solar Panel.
With those two pieces of information, follow the steps in this infographic to determine if you need to use fuses in your solar array:

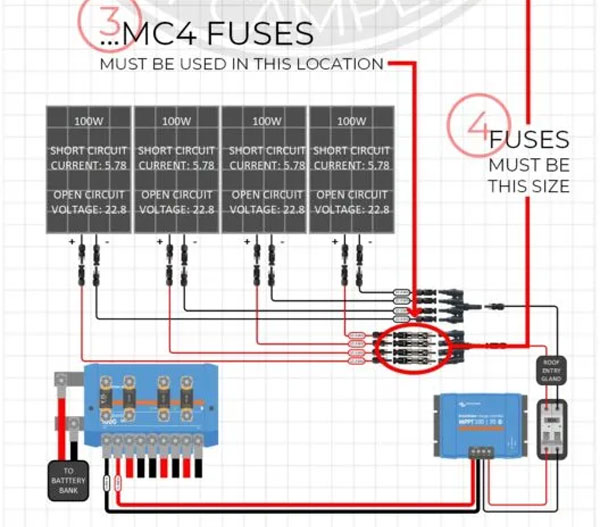

Why Must you Fuse a Solar Array?
In the event that your solar array needs to be fused because the Array Short Circuit Amperage is greater than the Panel maximum series fuse rating… you must fuse your array at the point where the panels or series strings get combined to prevent potential fires or overheating due to a faulty panel. Here is what happens in an un-fused array if a short were to somehow happen inside of the panel:
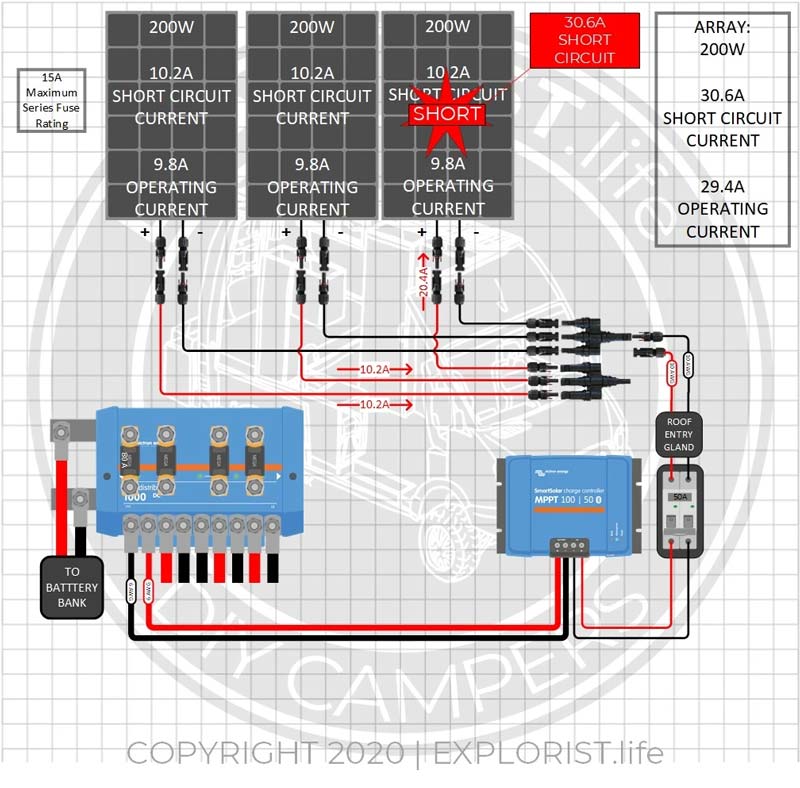
In the event that panel #3 develops an internal short or fault of some kind… panels #1 and #2 would seek out the path of least resistance (the point of the short) to complete their circuits). This means that there would be 20.4A flowing to panel #3, combined with the 10.2A FROM panel #3 where there could POTENTIALLY be 30.6A flowing through the short, which is over 15A higher than the max amperage rating of the panel and is more amperage than the panel is designed to handle.
Now… What if there were fuses attached to each of the positive wires from each solar panel where they connect to the MC4 Combiner?
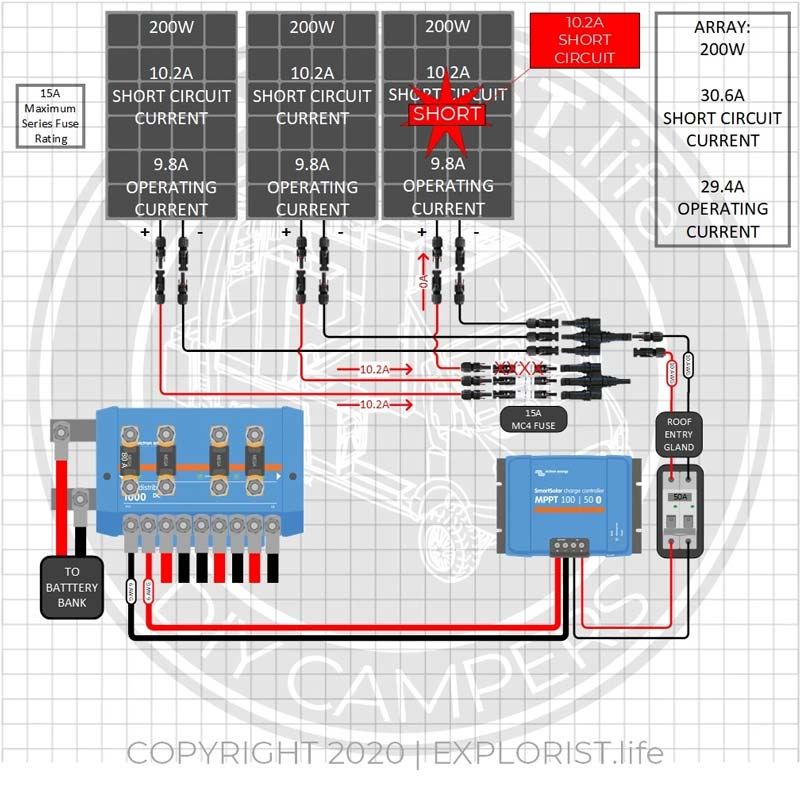
In the event that panel #3 develops an internal short or fault of some kind… panels #1 and #2 would seek out the path of least resistance (the point of the short) to complete their circuits). This means that there would be 20.4A flowing to panel #3 EXCEPT, that since we installed a 15A fuse protecting panel three’s circuit… that fuse would blow and isolate the problem panel to a short circuit that is within the maximum short circuit parameters of that panel.
That is why, by code, fuses are required in this array.
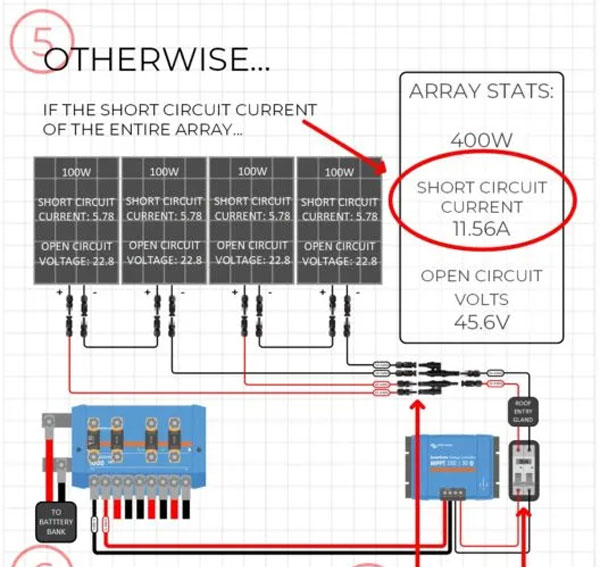
Why Would A Solar Array NOT Need to Be Fused?
If the Short Circuit Current of the solar array is less than the Maximum Series Fuse Rating of the solar panel, the array does NOT need to be fused. Fusing this type of array adds no additional protection or benefit, and here's why:
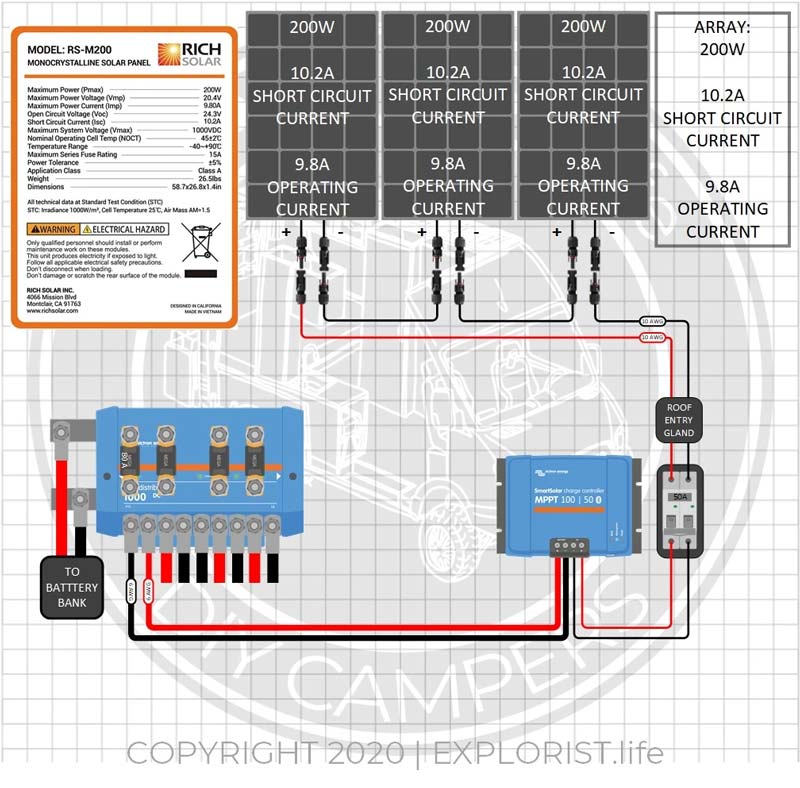
The diagram above shows 3x 200W panels wired in series. Each solar panel has a short circuit current of 10.2A, and operating current of 9.8A, and a Maximum Series Fuse Rating of 15A.
Since the Maximum Series Fuse Rating is 15A, we know that the wires, diodes, connectors, and other internal components of the actual solar panel can handle a max of 15A.
If a short circuit or other malfunction were to happen inside of one of the solar panels, since the short circuit current of the array is 10.2A, it’s safe to say that the panel itself is designed to handle this short circuit event as the short circuit current cannot exceed the maximum fuse rating of the panel.
Now… What if you just wanted to add a fuse ‘just to be safe’:
Ultimately… it wouldn’t do anything… In the event of a short circuit, 10.2A would flow. Under normal operation, 9.8A is flowing. Sure, a 10A fuse would indeed be between those two values, but the difference of .2 amps in either direction would either:
• Never allow the fuse to blow, or…
• Make the fuse constantly experience nuisance blows under normal operating consitions.
This is why a fuse, by code, is not required in this scenario.
Electrical Code vs Real World Discrepencies
Sometimes, there will be a discrepancy between what would happen in a real-world scenario and what is required by code. When this happens… ALWAYS abide by electrical code. Electrical code is sometimes a bit more conservative but is there for a reason.
Here is an example of a setup that would NOT benefit from fuses, but DOES require fuses according to electrical code.
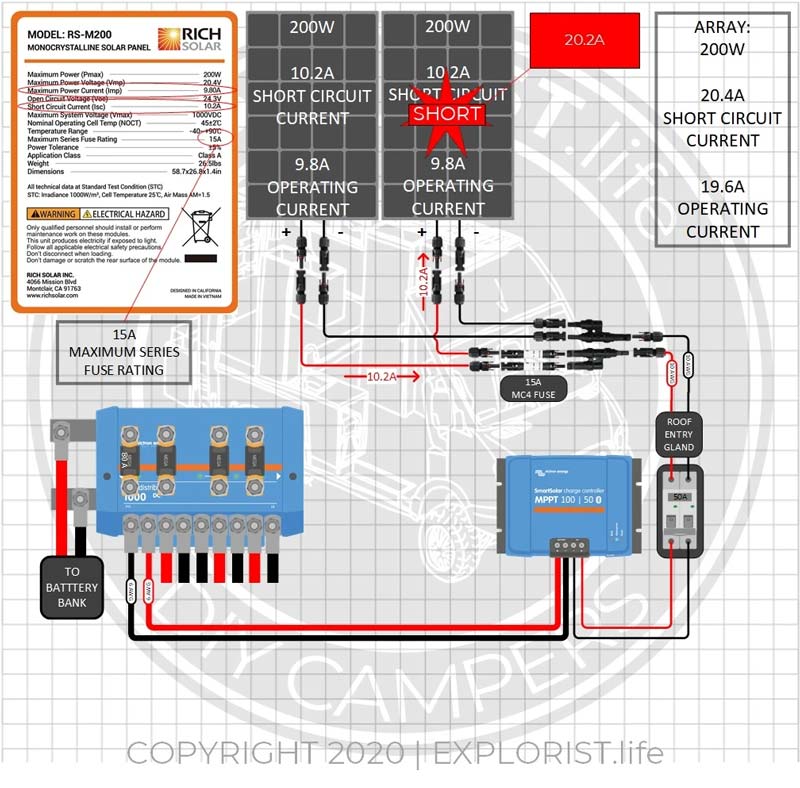
This scenario WOULD indeed require use of fuses in this array because the array short circuit current of 20.4 is greater than the 15A Maximum Series Fuse rating of the panels used.
In the event that panel #2 had an internal fault, the power produced in panel #1 would seek out the path of least resistance and flow into panel #2. This would mean that the area of the panel experiencing the fault would potentially have 20.2 amps flowing to the affected area.
Although there are 15A fuses in the proper locations, the current going from panel #1 into panel #2 would not be enough to blow either of those fuses.
Although this is not ideal, it’s nearly impossible to avoid when using two panels or two series strings in parallel and this setup is NOT forbidden by the National Electric Code so it's one of those things you just have to sit back and say; It’s fine. If it WASN’T fine… there would be an electrical code or standard saying something about it.
Fusing a Camper Solar Array – Final Thoughts
Faults in solar panels are quite rare. There are diodes in MOST solar panels that do not allow most of the above scenarios to happen. Fusing is required for a redundancy in the event that one of the diodes fails or something else goes wrong with the panel. There isn’t much to a solar panel. It’s pretty much just a bunch of Silicon cells fused together between some laminated glass connected to some diodes and wires. Even if a cell burns out, usually the panel will still work. But… Since the National Electric Code specifically makes a call on the issue of fusing an array, we really should follow that in our attempt to design and build a high end camper electrical system.





